Business plan is the backbone of every industry- micro, small, medium and large. To ensure success, every business plan has to be based on bare facts rather than imaginary projections and erroneous understanding of prevailing market conditions.
An excellent business plan helps everyone- owner and employees as well as associates and customers.

Golden rule of a business plan
The golden rule while drawing an excellent business plan is procuring all required data. American academic and professor emeritus at Harvard Business School, William A. Sahlman says a great business plan is the one drawn by answering several pertinent questions.
Sahlman, explains, these questions are based on four vital elements of business: the people, the opportunity, context and possibilities of reward and risk.
Word from Harvard
“What’s wrong with most business plans? The answer is relatively straightforward. Most waste too much ink on numbers and devote too little to the information that really matters to intelligent investors.
As every seasoned investor knows, financial projections for a new company – especially detailed, month-by-month projections that stretch out for more than a year – are an act of imagination.
An entrepreneurial venture faces far too many unknowns to predict revenues, let alone profits. Moreover, few if any entrepreneurs correctly anticipate how much capital and time will be required to accomplish their objectives.
Typically, they are wildly optimistic, padding their projections. Investors know about the padding effect and therefore discount the figures in business plans,”
William A. Shalman, in his widely acclaimed article titled ‘How to write a great business plan.’
Regardless of your geographic location, following these basics is essential for every business plan- traditional or start-up. The guidelines we provide are accepted worldwide for making an excellent business plan.
However, some variations may occur, depending upon your geographic location.
Guard Your Business Plan
As a general rule, business plans must be printed on business stationery. This lends it credence and accords it the status of an official document. A business plan is confidential document.
Hence, you need to take extra precautions to ensure it is not accessed by unauthorized persons. A business plan or any of its components, if leaked inadvertently or deliberately, can have disastrous effects on your enterprise.
Business Plan Formats
Broadly speaking, there are three main formats for drawing a business plan.
- Traditional Business Plan.
- Start-Up Business Plan.
- Expansion & New Project Business Plan.
You can either select the traditional business plan, start-up business plan or Expansion and New Project Business Plan, according to requirements.
Traditional Business Plan
A traditional plan is best suited for existing businesses.
Traditional business plans generally carry lots of details including vision and mission, history, past financial performance, product or service profiles, customer portfolio, details about staffing and future recruitment as well as projected growth in terms of clientele and revenue.
It also takes into account prevailing market conditions. Projections are based on various considerations including political and economic scenarios as well as existing and anticipated competition.
How to make an excellent business plan
Owners seeking funding for expansion of business or new projects can draw a traditional business plan. Here we provide some guidelines to make an excellent business plan.
Some of these elements are common to all- Traditional, Start-Up and Expansion & New Projects business plans.
Vision and Mission Statements
These are two distinct and separate statements. In the vision statement on a business plan, outline what objectives the company wants to achieve over length of time.
A vision statement should be written with clear perspective of other elements mentioned below. The mission statement also has to be sober and state why your company is in that particular business.
Be very realistic in writing the vision and mission statements. These are the first lines that anyone within your company, business associate, financer or investor would read.
Company Profile
The first step to make an excellent business plan is by writing a detailed profile of your company, regardless whether it is an existing business, start-up, expansion or new business.
Begin by writing a proper vision and mission statement. Give detailed information about products and services the business is offering or plans to launch.
Include your personal educational qualifications, experience and expertise in the particular field of business. Existing businesses as well as companies looking for expansion or opening new projects can add details about the leadership team.
Financial Information
Figures, for obvious reasons, speak louder than words. Extant businesses and those looking for expansion or new projects should include verifiable financial data.
This includes funding sources, assets, liabilities, taxes and other statutory charges, salaries as well as profits. Include brief details about your financials.
Market Scenario
As investor, you would definitely have sufficient knowledge about the market and the position of your business. Further, every business will keep itself informed about the latest market scenarios, happenings, government policies and other details that directly impact a business.
Writing these while making an excellent business plan also helps you review your company performance. Additionally, for those seeking investments and funding, it creates a good impression among prospective financers.
Financial projections
You can include projected growth and revenue for the running and upcoming financial year. Base your financial projections upon competitive advantages that your company has over rivals.
Details projected growth and methods you will use are vital for those seeking funding or external investment. All financial projections are to include anticipated expenses, expected Return on Investment (ROI), incidental expenditure, taxes and other charges.
These are to be reflected against projected profits for the current and forthcoming financial years. If you have astute knowledge about the market scenario, you may include projections for three to five years.
The US-based Small Business Administration recommends small business plans to include balance sheets, and cash flow statements for the last three to five years.
It also asks small business plan writers to include details of loans and collaterals.
Your Team
Include details about number of employees and their specific roles in the organization. This is where William A. Sahlman’s question about people becomes pertinent.
Having a good team and mentioning it on a business plan also helps attract funding, if needed.
If you are a start-up or looking to launch new project or expand your business, inform your financers about who will lead and key management figures. Provide their details such as education and previous experience, role they are expected to play in your business.
Legal Compliance
A new business plan has to include all documents or details about legal compliance.
This includes licenses procured from the government and other authorities such as registration, tax certificates, memberships of trade bodies, environmental clearances if applicable and others.
Legal compliance is something that financers look for before investing into any new business, project or expansion plans.
Business Offerings
Describe in-depth the nature of products or services you offer. Include details about how and where these products are manufactured or the system used to provide services.
Add notes about salient features of your products or services. Mention explicitly how your product or service helps clients. Businesses developing new products and services can also include their anticipated launches.
For new business plans, giving in-depth information about business offerings is something that can create a good brand image and attract funding, if required.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
For small business plans and new business plans, including a proper marketing and sales strategy is inevitable. Indeed, this is the very backbone of the business.
Unlike business plans of large companies, small business plans and new business plans do not have well defined marketing and sales strategies.
This puts you at severe disadvantage when seeking funding. Indeed, start-up business plans also need to include a proper marketing and sales strategy.
Here, you can discuss steps taken to promote your products and services, effectiveness of these measures, promotional campaigns, adapting current marketing and sales strategies for future and challenges faced.
Advertising, website and Social Media
Obviously, most companies nowadays have a website. Highlight features of your website such as online forms it provides for business enquiries, customer care, product and service offerings, company news and other relevant information.
Every business needs advertising. With social media emerging as preferred media for customer outreach, millions of companies rely upon Facebook, Twitter, WhatsApp, Instagram, Pinterest and LinkedIn.
A plan for extant businesses can include details about how much the company spends on advertising. Give details about where you advertize- newspapers, TV and radio, digital media.
Provide detail any blogs you own or those where your company, its products or services feature.
Startup Business Plan
Understandably, writing a startup business plan requires more research. Indeed, it has to be very comprehensive since most start-ups look for venture capital, crowd funding or bank loans as seed money.
Alternatively, they also look for funds to sustain the business. While you can add some elements of the traditional business plan, there are certain specifics you will also have to highlight.
Please note, it is imperative to include relevant information from traditional business plan such as staffing, key staff and leadership, projected financials, sales and marketing strategies among others, in a start-up business plan.
Contacting a good start-up incubator for drawing a business plan can fetch you the desired results.
Nature of Business
To be attractive, any startup has to be unique. Meaning, your offerings have to differ vastly from those available from established companies and competitors.
After adding the mission and vision statement and other relevant details from a traditional business plan you can speak about why you think your business will succeed.
Business Associates
Start-ups general do not operate alone during the first couple of years of inception. They require other businesses such as suppliers, logistics, warehousing, IT support and other infrastructure to support the business.
While including these strategic partners for your start-up, also mention details of the roles they will play in your business.
Competitive Advantage
As mentioned earlier, nobody would be interested in funding a startup that does not have a clear competitive edge in the market. Here, you will need to include details about why your product and service offerings are better than competitors.
Augment this with few lines about realistic quality assessment of your offerings vis-à-vis those of other firms in the same industry.
Resources
You may have excellent academic qualification and expertise in your chosen start-up field. This is one of the resources you can draw upon, provided your self assessment is not exaggerated.
Another important resource you need to mention in a startup business plan is the expertise your associates or partners or employees have brought in.
Physical resources including funding from your savings can also be safely mentioned on a start-up business plan. Intellectual property rights held by your start-up count as a key resource and hence, it is vital to include it on you start-up business plan.
In a nutshell, write about each and every resource that your start-up has and can reliably draw from during the course of operations.
Financial Indicators
Before launching a start-up and drawing a business plan, you will require in-depth studies about how the market for your product or services is shaping up, government policies and some insight of future developments.
Draw your financial indicators based upon facts. These include inherent strengths and weaknesses of your start-up and anticipated market share. Remember, these financial projections have to be realistic to appeal to financers.
Inflated financial projections and claims in a start-up business plan tend to put off investors, since they will also conduct independent research into the market.
Target Customers
While writing this element of a start-up business plan, you need to be extra cautious. Your target customers will already have other suppliers who are already flourishing in the market.
Speak about various workable strategies your startup intends to adopt to wean some part of business from these established suppliers. Talk about what value you can add to business or life of your targeted clientele.
Including details such as how your firm intends to deal with customers- personally through representatives or online and the customer experience you intend offering are also vital components you need to include in this segment of your start-up business plan.
Delivery Channels
In this section, you have to provide specific details about how your product or service will be delivered to customer.
This section includes details about ways and means you will adopt to inform customers about your offerings, technology or techniques used to place orders, systems that will help your start-up deliver the product or service as well as after-sales customer care.
Generally, every start-up uses multiple channels such as person-to-person contact, email marketing, online orders and home delivery services. Include these intricate details in your start-up business plan.
However, ensure that your delivery channels are efficient as well as cost effective. Often, delivery channels can prove expensive and eat into overall profitability of start-ups.
Costs
Another significant component you need to include on a startup business plan concerns costs involved in your operations. Obviously, you will incur some expenses while launching a start-up, even if you plan to locate your office at home.
Your service delivery channels will constitute major costs. Advances paid to business associates to ensure continuum of supplies or services, legalities and other inevitable expenditure all adds to cost of your start-up during the launch period as well as the first year of operation.
It is fairly simple to get a clear indication about what your launch and operational costs will be during fledgling stages of the start-up. However, while mentioning this, make a generous allowance for any unforeseen expenses.
Staffing
Staffing a start-up is something most entrepreneurs overlook while writing a good business plan. Staff salaries and perks consume a lot of capital.
Additionally, financers will also want to know caliber of the staff that will operate your start-up. Meaning, they will look into academic credentials, experience and value the staff can add to your venture.
Wherever possible, include CVs of key persons in your start-up while highlighting their achievements at previous roles. Also add a summary of their duties and why a particular staff is essential for success of your start-up.
Should the start-up be capable of generating employment, mention this explicitly, since some governments and departments offer incentives for job creating ventures.
Sustainability
A report on Forbes states, 90 percent of all start-ups fail for a variety of reasons such as irrelevance to the market they operate, insufficient funds, wrong financial projections, inability to keep abreast with technology and a plethora of others.
Sustainability is the key to success of any start-up venture. Financers including venture capitalists, banks and crowd-funding platforms will study sustainability of your start-up before investing anything as much as a single cent.
Hence, include every possible yet verifiable reason why your start-up can be sustained beyond the first year in your new business plan. This ensures VCs and other lenders that funding your start-up could be profitable.
Expansion & New Projects Business Plan
Expansion and new projects are something that only established businesses venture into. A small or medium enterprise would wish to expand its operations to maximize profits and consolidate market position.
On the other hands, larger organizations would add newer projects for diversifying their business portfolios. In such instances too, they need to make an excellent business plan.
Reasons to Expand
You would definitely have genuine reasons for expansion of your small or medium business. Cite these reasons clearly. Speak about the popularity of your products in the existing markets and their demand in areas where you wish to venture.
Accurate information about prevailing conditions in these proposed markets is vital for your success and to attract any required funding.
Infrastructure for Expansion
Unless you can cater to the newer markets from your existing facilities, you may require new infrastructure. More so if you intend entering markets that are distant from your head quarters.
Required infrastructure may include production units, logistic chains, service channels and representatives. Good studies into these requirements will enable you draw an excellent business plan for expansions.
Business plan for a new project or diversification also need to mention these relevant details.
Funding
Writing about how to intend funding the expansion is of course vital. State whether your existing business will fund the expansion.
Should you require external financing, be specific about what components of expansion for which you are seeking funds. You may require funding to open a manufacturing unit or office as part of expansion.
New Projects
As mentioned earlier, new projects are part of diversification by an established enterprise. For example, a skincare major may wish to diversify into food products to cash-in on its reputation.
Hence, mention what your new project is all about and cite exact reasons about why you intend to diversify.
Competitors
Local companies operating in geographical or business areas where you wish to expand will usually be well established.
Parochial attitudes of populations also decide popularity of a particular brand of product or service as people tend to be loyal to local companies than those with headquarters located far away.
Hence, expansions or new projects can often be stonewalled by these unexpected factors. Include how you intend to circumvent such bias and position yourself in a hitherto unexplored market in your expansion business plan and new projects business plan.
Business Plan Templates
Hundreds of readymade business plan templates can be downloaded free from the Internet. They can be used to make excellent business plans provided you are armed with the required information.
There are no set rules about how to write an excellent business plan. However, your business plan needs to incorporate these basics:
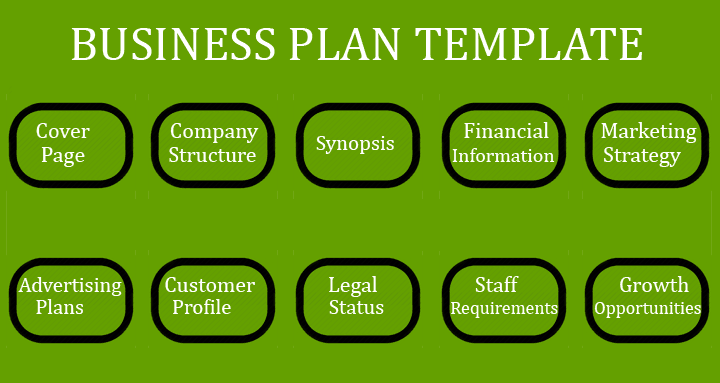
Cover Page: List your company’s name, logo, contact details and sphere of operation.
Synopsis: Give a brief description of your business, its relevance to the market and uniqueness of your products or services.
Company Structure: Mention your academic achievements, experience and that of key personnel in your company.
Financial Information: Latest financial information if your business is established. Alternatively, start-ups can provide details about seed money and how they intend to fund the business.
Marketing Strategy: Give details about how you intend to go about popularizing your product to target clientele and the channels you will deploy.
Advertising Plans: Speak about the use of advertisements, social media and blogs your company plans to use for customer outreach.
Customer Profile: State the type of customers- such as industries, households, individuals, educational institutions and others that your company already has on board or wishes to attract for future business.
Legal status: Include all details such as commercial registration, licensing, compliance with industry standards, international certifications and other information that gives your company complete legitimacy.
Staff Requirements: Include details about your existing staff and their roles in the organization. Highlight their achievements at previous jobs and in your business. Also discuss projections for staff in foreseeable future.
Growth Opportunities: Any business plan that excludes growth opportunities is absurd. While it is difficult to project growth due to uncertainties in policies and politics, you can write about these based on past and current performance in the market.
Financing Details
Generally, small business plan, start-up business plan or new business plan will have to incorporate a funding proposal, unless you are capable of financing the venture through savings or borrowings from relatives and friends. Usually, an excellent business plan will include these elements:
- Amount of money you will invest.
- Funding needed from external sources.
- Ways and means you will deploy to get financing.
- Previous records of loans or borrowings from banks, venture capitalists or crowd-funding platforms and other lenders, if any.
- Return on Investment made to lenders, where you were funded by an external source.
Seeking Funds in Business Plan
While writing a funding proposal, specify how much money you will need over the next three to five years for new business/start-up or for expansion and new projects.
Explicitly state how this money will be utilized and need for this expense.
Next, mention the sources from which you intend to raise the funds such as bank loan, venture capital or crowd funding, mortgaging or selling assets.
Be very specific about how you intend repaying the money with a tentative schedule of installments.
Consider staff salaries, operational expenses, taxes and legal obligations as well as costs on logistics, infrastructure and other essentials of your business before arriving at Return on Investment you can pay to venture capitalists, crowd-funding platforms, banks and other lenders.
Seek repayment ‘holidays’ or exemption from paying installments on borrowings for a specific period such as a year. This will allow you adequate time to garner funds needed to service the loans.
Cite various sources and interest rates/ Return on Investment they are seeking from your business. This will help you get competitive rates, provided you make an excellent business plan.
Business Plan, Feasibility Report & Project Report
Often financers seek a detailed project report and feasibility study along with a business plan. Such a demand can arise from banks, venture capitalists or crowd-funding platforms where the amount sought is high or you submit a business plan for some unique enterprise.
The three are separate documents. A feasibility study has to be done and submitted by a qualified assessor that can include an industry expert, Chartered Accountant or engineer with relevant experience.
Project reports are written by people skilled in assessing projects and writing in-depth, the various aspects it involves.
A simple business plan can however be penned by you, as owner or entrepreneur.
In conclusion
Funding nowadays is not easy to come across due to thousands of start-ups mushrooming across the world. Banks are reluctant to lend due to high volumes of Non Performing Assets (NPAs).
In this scenario, an excellent business plan can help you procure required funding.
Other than merely a fund-seeking document, business plans also serve as guidelines to the owners, key staff and employees of an enterprise. It enables them to get a clear vision about where their employer wants to position the company and subtly informs them of duties they need to perform.
An excellent business plan helps boost staff confidence and speaks volumes of good to business associates. You can make a good business plan by following some of the above mentioned steps and help your enterprise grow.